Gilsonite


Gilsonite (Natural Bitumen)
Gilsonite or mineral bitumen is a solid hydrocarbon and a type of asphalt, which is often found in natural bitumen mines and is actually hardened crude oil. Gilsonite is found in underground mines as a black and hard substance with a shiny surface. Due to the fragility of this material, its application is often in the form of powder, which has a dark brown to black color.
Gilsonite is a black substance that has high brittleness. This material, like glass minerals, has a high luster. Gilsonite is often available in lump and powder forms. The production and process of obtaining powder with micron dimensions is called micronization. By using meshing, micron-sized powders can be separated. Smaller meshes produce smaller sizes of Gilsonite powder particles. Powders can be presented with different meshes. 60-100-200-325 meshes are often used to produce Gilsonite powders.
Gilsonite chemical elements
The main constituent elements of Gilsonite are carbon and hydrogen. For example, a sample of gilsonite consists of more than 80% carbon and 10% hydrogen. Other components of Gilsonite include sulfur, nitrogen, calcium oxide, titanium oxide, garnet, magnesium oxide, iron, potassium oxide, phosphorus pentoxide, manganese oxide and sulfur trioxide.
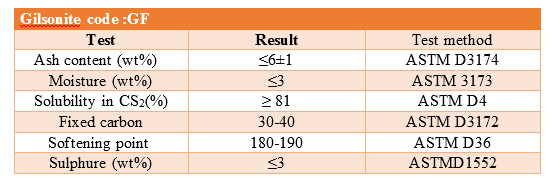
Physical analysis of Gilsonite
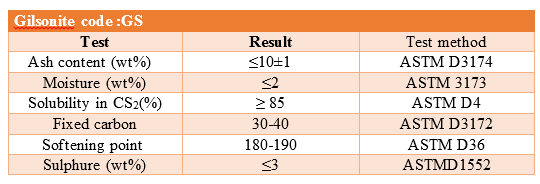
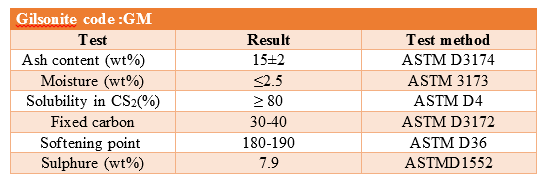
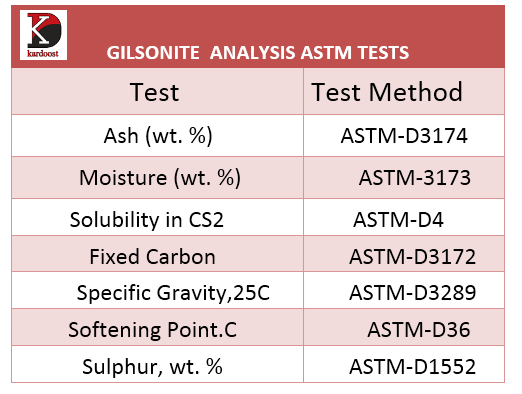
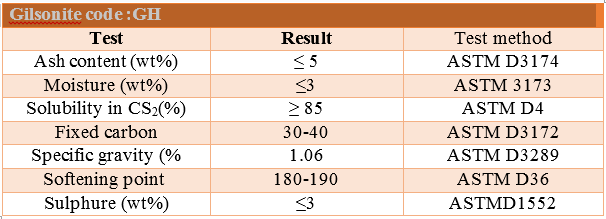
For accurate analysis of Gilsonite, physical parameters related to its quality should be investigated. Some of these parameters are shown in the table below
The important physical parameters in determining the quality and nature of Gilsonite are the opposite photo:
1- Ash Content:
Measuring the amount of bitumen ash is the most important parameter that determines the quality of bitumen. This parameter determines the degree of impurity or purity of Gilsonite. The lower the ASH or ash in the sample, the higher the quality of the product. Gilsonites in Iran have an average of 15% ash. Different nests are used in different applications and industries. Ash is measured and calculated using the ASTMD3174 standard test, which is used to measure coke and coal ash.
2- Solubility:
Pure bitumen can be obtained by using special solvents. If we dissolve a sample of bitumen in any of these materials, its impurities will remain and from there we can determine the degree of purity of the bitumen.
Solubility in carbon disulfide (CS2): one of the applications of gilsonite is its use in preparing asphalt. Carbon disulfide is used to combine Gilsonite with bitumen and asphalt. Therefore, one of the important parameters for determining the properties of Gilsonite is its solubility in hydrogen disulfide, which is determined using the ASTMD4 standard test, and the net weight of undissolved materials is calculated, and as a result, the solubility is calculated.
Solubility in carbon tetrachloride (CCL4): Carbon tetrachloride is used in many applications of Gilsonite in chemical industries, such as wax, resin, etc. For this reason, one of the calculated parameters for Gilsonite is the solubility in carbon tetrachloride. Solubility in CCL4 is measured and calculated using ASTMD3467 standard test.
Solubility in trichlorethylene (TCE): another material that is used like carbon disulfide in asphalt and pavement industries to combine bitumen with gilsonite is trichlorethylene. The solubility of Gilsonite in this material is determined using the ASTM2042 standard test.
3- Softening Point:
The softening point is the temperature at which the bitumen turns from solid to liquid when bitumen reaches that temperature. The higher the degree of bitumen softness, the less sensitive it is to temperature changes. The degree of softness of ordinary bitumen is about 60 to 70. One of the measured parameters for gilsonite is the degree of softness, which is determined using the standard ring and ball test with the ASTMD36 standard at a temperature of 30 to 157 °C.
4-Specific Gravity:
The specific gravity and density of the material are important physical parameters that are measured and calculated using the ASTMD70 standard test.
5- Pure Carbon (Fixed Carbon):
The amount of carbon, as the main and dominant ingredient of Gilsonite, is a key physical parameter. The amount of combustible carbon in gilsonite after removal of ash, moisture and volatile matter is measured and calculated using the ASTMD3172 standard test.
Applications
It has been reported that Gilsonite has many and valuable uses in various industries such as paint, resin, asphalt, road paving, casting, chemical materials, drilling mud and cement, and rubber. Due to the fact that Gilsonite is a natural and non-toxic substance, its use is increasing. Based on the studies carried out, the main applications of Gilsonite can be introduced as follows:
Gilsonite is used in the production of drilling mud and cement slurry. It is used in drilling fluids for cementing oil wells. This mineral is a unique and stabilized combination of gilsonite grades to provide optimal and appropriate action in drilling mud to stabilize the shale walls of oil wells. This substance reduces the weight of the slurry.
The use of Gilsonite in drilling has advantages such as the following:The resulting slurry has a low density without adding a large volume of waterThis material is compatible wit other additives and is resistant to acidic, alkaline and corrosive materials Resists premature grout hydrationThe temperature range of its use is wide It resists medium pressures caused by water absorption, but it is soft enough to change shape due to pressure
Due to staying and pressure, it does not become lumpy or colonized. It is resistant to dissolution by oil During the cementing of oil wells, due to the property of plastic flow, it closes the seams and cracks of the well.
asphalt production
Since gilsonite is highly hydrophobic and resistant to acid and base, it is generally used in the preparation of asphalt and Roof insulation. One of the distinctive features of gilsonate materials is their solubility in non-polar solvents such as carbon disulfide, toluene, and molten bitumen. is.
Gilsonite is considered a suitable modifier for refinery bitumen, especially asphalt and Roof insulation, due to the presence of polymeric hydrocarbon materials. Gilsonite also reduces the degree of penetration, increases the viscosity, increases the softening point, and increases the heat resistance of refinery bitumen.
Gilsonite is used as an agent to increase efficiency and efficiency in asphalt mixture. Asphalt mixed with high-quality Gilsonite, without the need for other modifiers that are added to the asphalt in the form of powder, becomes completely uniform. Gilsonite in general in “SBS” modifiers, either partially or as a supplement, can replace asphalt polymers in terms of value and price.
Asphalts modified with Gilsonite have higher stability, less deformation, ability to withstand lower temperatures and more resistance to water and less permeability than asphalts not mixed with Gilsonite. Gilsonite is used as a preservative in hot mixes for paving. In fact, the main task of Gilsonite in this application is to improve the stability of pavements and their resistance to deformation, which increases the ability to bear the load, and they are used in areas under high pressure and stress.
The presence of sulfur-containing compounds in Gilsonite also increases the strength of Gilsonite for use in asphalt. In general, the use of Gilsonite in asphalt can have the following advantages:
Reducing the degree of penetration of bitumen
Increasing the softening temperature of bitumen
Increasing the viscosity of Brookfield bitumen
No need for other polymer modifiers to modify bitumen.
Higher stability, less deformation, more resistance to water, ability to withstand low temperatures, are the characteristics of asphalt made with bitumen modified by natural bitumen.
Increased load bearing capacity
The lowest proportion of natural bitumen compared to other modifiers
Casting
Gilsonite is used as a carbonate additive in casting sands, which creates smoother mixed plates, and as a sea coal adhesive on gray iron molds. Gilsonite special companion is used for casting sand, which reduces the defects at the end of the casting operation.
It also improves mold release. Gilsonite is also used in casting as a binder to shape metals. Gilsonite is used for mixing with chemical compounds such as magnesium and hydrated lime for desulfurization in the steel industry.
Ink and color
Black and brown pigments are extracted from Gilsonite, which are used in the preparation of printer inks. Iranian gilsonite resin is widely used as carbon black to produce black ink and viscous ink. Iran’s gilsonite resin competes very well with petroleum-based hydrocarbon resins, phenolic resins and metal resins, which can be used at the price of all the mentioned items with different concentrations. Different concentrations of this substance are used to produce special inks with high brightness
. A special type of Gilsonite is also used in the production of black asphalt paints and polishing oils. It can also be used to prepare a black-brown colored solution, which is used in the bitumen coating of gas pipes, sewage, etc. This product is used to cover external surfaces, also to make surfaces resistant to acid, car chassis coating, metal structure coating. It is used as a low-cost alternative to other resins in black ink compositions.
Production of coke
Gilsonite can be used to produce coke in the steel industry, which has a higher carbon content than coal.
It is also possible to prepare coke from some of its types.
Bitumen is mixed with coal that has weak coking properties and coke is prepared from it. The obtained coke is often used in the sugar industry. Also, from its sulfur-free types or after desulfurization, a type of coke called needle coke is prepared, which is widely used in electric arc melting furnaces.